Verb-ish Models for Verbalization: Give Us Back Our Verbs!
Excerpted from Chapter 4, Business Rule Concepts: Getting to the Point of Knowledge (Third Edition), by Ronald G. Ross (August 2009). ISBN 0-941049-07-8 http://www.brsolutions.com/publications.php
Let me tell you something we have learned from our work on business rules. The world's leading cause of ambiguity in expressing business rules — and other requirements — is missing verbs. The following example illustrates.
Business Rule: An order must not be shipped if the outstanding balance exceeds credit authorization.
As a first-cut statement, that's perhaps not bad. The more you read it, however, the more ambiguity you'll see. Clearly, some important ideas are hidden or missing. For example:
The outstanding balance of what? …order? …customer? …account? …shipment?
The credit authorization of what? …order? …customer? …account? …shipment?
The hidden or missing ideas are all verb-related. To eliminate the ambiguity, the relevant verb concepts — a.k.a. fact types — must be discerned, then the original business rule restated. Suppose the relevant fact types can be worded as follows:
customer places order
customer has credit authorization
customer holds account
account has outstanding balance
Using RuleSpeak[1] the business rule can now be restated as:
Revised Business Rule: An order must not be shipped if the outstanding balance of the account held by the customer that placed the order exceeds the credit authorization of the customer.
Although the resulting statement is a bit wordier, it is far less likely to be misunderstood, misapplied, or mis-implemented. It is now enterprise-robust. Two key insights:
- Wordings for fact types are generally expressed using verbs. Note in particular the verb holds (or held) and the verb places (or placed). (I'll come back to the pesky preposition 'of' later.)
- Wordings for relevant fact types should always appear explicitly in expression of business rules. For that matter, wordings should appear explicitly in any form of business communication you want to be unambiguous, including IT requirements.
Given that verbs are so crucial to effective business communication of all kinds, you might question why data models and class diagrams haven't focused more directly on them. The answer, quite simply, is that these tools weren't created for that purpose. They are first and foremost design tools for IT professionals.
What do IT professionals design? In general, they are focused on implementing data containers (e.g., tables) or software objects. That focus leaves them noun-ish, but not also verb-ish. The price we are paying for that shortfall in poor business communication practices is huge.
How can the problem be fixed? The answer is simply that verb-ish things should be included alongside noun-ish things as a fundamental part of any structural modeling. This article explains how.
What It Means to be Verb-ish
Many IT professionals associate verbs only with processes, as in "take order" or "pay invoice" or "hire employee." Nothing in the real-world meaning of 'verb', however, limits its use solely to that concern. Have a look at the definitions of 'verb' and 'predicate' in the box below.[2] Restricting use of verbs only to the naming of processes, tasks, or actions is very unnatural.
Verb: a word belonging to that part of speech that characteristically is the grammatical center of a predicate and expresses an act, occurrence, or mode of being ... Predicate: [2] the part of a sentence or clause that expresses what is said of the subject and that usually consists of a verb with or without objects, complements, or adverbial modifiers |
Experts in the field of linguistics explain that verbs play a far more crucial role. For example, Steven Pinker writes,[3] "A verb, then, is not just a word that refers to an action or state but the chassis of a sentence. It is a framework with receptacles for the other parts … to be bolted onto." Without verbs, literally there are no sentences.
Sentences are how you communicate effectively. Sentences are what you're reading right now. A well-written business rule is always a sentence. In general, all business communication and many forms of business requirements should be sentences. When you start looking at things that way, it becomes obvious that verbs must be an integral part of any structural model.
Let's take a closer look. Without going too deep into philosophical questions, every verb generally has two sides. Yes, you can think of a verb as designating some action. But you can also think of a verb as designating something you can know. Take, for example, the verb 'to place', as in a customer placing an order. You can look at 'to place' from two perspectives, both valid:
- There is something a customer can do — i.e., place an order. That's an action or process.
- There is something that can be known — i.e., that a customer can place an order. That's a fact.
The first perspective, of course, is very important. No one is saying you shouldn't model processes. But taking even a cursory look at other challenges facing businesses today suggests the second perspective is also crucial:
- Achieving reusability or sharing of data (data design).
- Providing high-quality information (business intelligence — BI).
- Expressing business rules (criteria for operational decisions).
- Eliminating stove-pipe products (product re-engineering).
- Retaining know-how (knowledge retention).
Verbs are therefore the point of departure for addressing a host of broader needs facing businesses today. Modeling the underlying verb concepts (as well as the nouns they involve) is the purpose of fact models. Think of a fact model as a verbal model, one serving for more effective verbalization of operational business knowledge. It's high time we focus on the basics of business communication as the starting point for everything we do or design.
Fortunately, fact modeling as a discipline has a long and solid pedigree. It's not something new; it's been around for decades. The gurus of this space include Terry Halpin[4] and Sjir Nijssen[5]; the standard for the space is SBVR.[6] Actually, this discussion features only two new things:
- RuleSpeak and the now in-depth understanding of how business rules should be based on facts and fact models.
- The conventions used in this article to represent fact models graphically. We[7] developed this graphical notation in large-scale client projects starting in the mid-1990s to provide a more business-friendly face for fact models.
Issues That Can Only Be Handled Well Using Verbs
Traditional data models and class diagrams fall short in a number of respects in their handling of verbs. The following discussion outlines three of these shortcomings, each addressed effectively in fact modeling. First, two quick points about terminology in the box below.
Verb: For convenience, I say verb although I really mean verb or verb phrase. For example, 'owns' counts as a verb, but in my usage so too do 'rides in' and 'is being actively marketed'. Verb Concept: SBVR has defined verb concept and fact type as synonyms. These two terms can be used interchangeably. A verb concept or fact type is always understood to include some relevant noun concept(s) as well as something verb-ish. So the verb 'owns' might be included in the expression of the verb concept (or fact type) 'person owns vehicle'. |
Unary Fact Types — Verbs about Only One Thing
A unary fact type always provides a simple yes-or-no answer to some basic operational business question. In other words, a unary fact type is always Boolean (i.e., true or false). The following example illustrates.
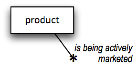
Figure 1. Fact model showing unary fact type.
Note on Notation The starburst symbol always indicates 'fact type'. Here, the starburst introduces the verb (phrase) 'is being actively marketed'. The line between the noun concept 'product' and the starburst means nothing on its own; it simply shows where the verb (phrase) fits into the diagram. |
The fact type worded 'product is being actively marketed' is unary because it pertains to only one noun concept, product. This unary fact type indicates that a given product either is or is not being actively marketed. The actual answer to the question, of course, depends on which particular product is being talked about.
Like any fact type, this unary fact type could be relevant to many kinds of business communications, including statements of business rules. The following sample business rule illustrates.
Business Rule: A briefing may be given only for a product that is being actively marketed.
Roles — Noun Concepts Whose Meaning Is All Tied Up with Verbs
Business people often have a special term for a noun concept they use only in the context of some particular fact type. The following example illustrates.
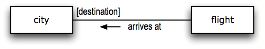
Figure 2. Fact model showing a role.
The fact type diagrammed above is: flight arrives at [destination] city. The term in brackets, 'destination', is simply a more specific term used to refer to a city when it is a city where a flight arrives. Such a role name designates the part (or 'role') the concept 'city' plays in the context of the fact type. It means nothing more than that.
Note on Notation Like for unary fact types, a line representing a binary fact type means nothing more than the verb used in its wording. The little directional arrow that appears alongside the line simply indicates how to "read" the fact type. The proper wording for the fact type above is therefore understood to be 'plane arrives at [destination] city' — not 'city [destination] arrives at flight' (obviously nonsensical). A starburst is usually omitted for a binary fact type since what the line represents is generally obvious from the context of the diagram. |
Roles are not the usual kind of noun-ish things IT professionals generally expect; that is, they are not 'normal' entity types or classes as understood in data models or class diagrams. Rather, the meaning of these noun concepts is inextricably tied to some verb (e.g., 'arrives at').
Role names are a particularly good way to handle terms that directly reflect the particular choice of verb in the wording of a fact type. For example, in the following diagram, the role name 'owner' directly reflects the verb of choice, owns.
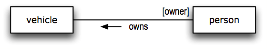
Figure 3. Fact model showing a verb-reflecting role name.
Like any other term, a role name is frequently relevant to many kinds of business communication, including statements of business rules. The following sample business rule illustrates.
Business Rule: A parking citation may be given only to the owner of a vehicle.
Reversal — Verbs of the Opposite Persuasion
Even if a data model or class diagram gives a verb in one direction of a relationship, it seldom gives it in the opposite direction. Or if it does, it merely offers a preposition. For example, in the following data model, the opposite direction of the verb 'is involved with' is labeled simply 'of'.
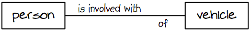
Figure 4. Data model showing a preposition for the opposite direction of a fact type.
Proper wording for the opposite direction of a fact type, however, is often needed to express business rules or to compose other kinds of business communication or requirement. The following sample business rule illustrates.
Business Rule: A vehicle must not transport more than 4 passengers.
In this business rule, the verb 'transport' is used to clearly express the appropriate meaning. Try substituting 'of' in some way into the statement and see how well that works to express the meaning. (It doesn't.) In fact modeling, stand-alone prepositions for fact types are considered lazyman's verbs. Literally, you can't make complete sentences with only prepositions!
Actually, the communication problem gets even worse. In the real world, people can be involved with vehicles in different ways. 'Passenger' in the business rule above suggests just one way. Suppose that people and vehicles can 'be involved' with each other in at least four ways:
- People own vehicles.
- People lease vehicles.
- People drive vehicles.
- People ride in vehicles.
In data models, such differential 'involvements' are typically handled using a type code treated as 'intersection data'. The following data model illustrates.
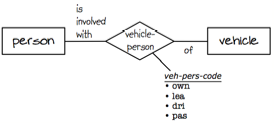
Figure 5. Data model showing a type code treated as intersection data.
This data model features a new noun-ish thing 'vehicle-person', in which the type code 'veh-pers-code' has been included. Four values of the type code are listed to distinguish the four kinds of 'involvements' from above.
Let's see what now happens to the expression of the passenger business rule. We started with this:
Business Rule: A vehicle must not transport more than 4 passengers.
Using the terminology provided by the data model, the rule might now be expressed like this:
Rule: A vehicle must not be of more than 4 people where veh-pers-code = "pas".
Do we really want business communications to sound like that?! No! The statement contorts the meaning (mangles the semantics) almost beyond recognition. Besides losing the clarity of 'transports', we've forced the business people to speak in terms of a type code. That's unnatural. This example clearly illustrates the difference between a true business rule (the original version) versus what must be considered a data rule or system rule (the mangled version).
To emphasize this latter point, let's consider a bit more complicated business rule pertaining to two kinds of 'involvements'. First, here is the rule verbalized as a business person might expect:
Business Rule: A person must not lease a vehicle the person owns.
Using the vocabulary of the data model above, however, we get the following verbalization:
Rule: A person must not be involved with the same vehicle where veh-per-code = "lea" and veh-per-code = "own".
Clearly, the more complicated the business rule, the worse the mangling. And a great many of your business rules are very complicated! Without further ado, let's simply agree that's awful and move on. The following diagram indicates how these semantics (verb concepts) would be fully handled in fact modeling.
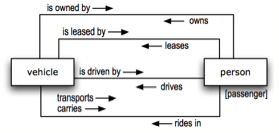
Figure 6. Fact model showing multiple 'involvements'.
Some key observations:
- Fact types are always bi-directional (or multi-directional) even if not worded as such explicitly. (All the fact types above have been worded in both directions for the sake of completeness.) Fact models then are very different from process models, which always designate uni-directional flows.
- Two or more noun-ish things can be related more than once if the meanings of the verbs are different. This differentiation has resulted in the four fact types above.
- Any verb concept can have a synonym if the meaning is considered exactly the same by the business. In the diagram above, for example, the verbs 'transports' and 'carries' are indicated to be synonyms in the context of the given fact type.
Now back to the business rules. The fact model gives us all the scaffolding we need to verbalize the business rules succinctly and naturally. You can verify that for yourself:
Business Rule: A vehicle must not transport more than 4 passengers.
Business Rule: A person must not lease a vehicle the person owns.
Using the fact model as a blueprint, we can have a real business conversation with business people and subject matter experts in natural language about whether these business rules are valid and complete. Indeed, business analysts should ask some hard questions, including perhaps the following.
- Is the person who drives a vehicle considered a passenger?
- Does the business rule also apply to buses, or just to passenger cars?
- Does the business rule mean a vehicle can't carry more than 4 passengers ever, or just at any given point in time?
- Can the same person be a passenger in the same vehicle more than one time over time?
- Why do we really care how many passengers ride in a vehicle?
The answers to these questions could well indicate that the current fact model is incomplete. For example, if the business rules are from a city government, we might actually want to talk about when to issue traffic citations. The actual business rules might be:
Business Rule: A passenger overload traffic citation must be written for a passenger vehicle carrying more than 4 passengers.
Business Rule: A traffic citation may be given only to a person driving.
The noun concept traffic citation (and related fact types) does not appear in the fact model above. Clearly, some work on that is in store. Now ask yourself this: Would you rather work this out before or after you get to a data model or class diagram? The answer, I think, speaks for itself.
My point is this. The fundamental problem in business today is not design or implementation of databases or systems. Rather, it is the challenge of business communication. If you can't clearly communicate (verbalize) what you know, you'll never get the database or system you want.
Where does that take you? Directly to writing complete sentences, which in turn brings you straight to verbs. There's simply nowhere else to turn.
More Ways in Which Fact Models are Verb-ish
Fact models are verb-ish in even more ways than discussed thus far. Two additional areas are examined next.
Objectification
In natural language, we often turn verbs into nouns or noun phrases so we can talk about them as things. Doing that is called nominalization; often the intent is to objectify[8] the verbs. For example, we might objectify the fact type worded 'person [owner] owns vehicle' into the noun-ish thing ownership. The following diagram illustrates, using a dotted line to show that the fact type has been objectified.
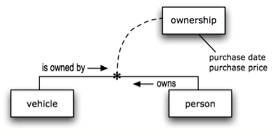
Figure 7. Fact model showing objectification.
Because objectifications (e.g., 'ownership') are things, they can have properties. For example, ownership might have the following two properties, as illustrated in the diagram.
- Purchase date — the date a given vehicle was purchased by a given person.
- Purchase price — the price paid for a given vehicle by a given person.
All these terms, including the one given to the objectification, are likely to be relevant to business rules. The following sample business rule illustrates.
Business Rule: Proof of purchase must be provided to establish ownership of a vehicle.
States
How do we talk about some potential state of something in everyday language? We naturally use a past participle, another verb-ish construct. The following diagram illustrates informally for the noun concept order.
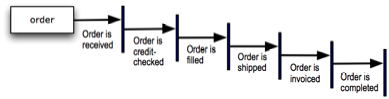
Figure 8. Informal representation of states for 'order'.
In this example, six states have been identified for the normal life cycle ('happy life') of order. Each has been identified using a past participle: received, credit-checked, filled, shipped, invoiced, and completed. A quick look at the definitions of 'past participle' and 'participle' puts this usage into perspective.[9] Note especially the words completed action — that sense is an important one for business rules, as we'll see momentarily.
|
Past Participle: a participle that typically expresses completed action … Participle [1]: a word having the characteristics of both verb and adjective; especially: the English verbal adjective ending in -ing or in -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n |
One especially important use of unary fact types in fact modeling is to represent states of noun-ish concepts, as the following formalization of the above diagram illustrates.
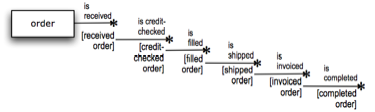
Figure 9. Fact model for the 'happy' states of 'order' using unary fact types.
Six unary fact types are represented in this diagram. Each unary fact type is given a wording that involves a past participle representing a particular state (completed action) in the life cycle of 'order'. Shown below each unary fact is a role name for an order in that particular state:
- A received order is an order for which 'order is received' is true.
- A credit-checked order is an order for which 'order [received order] is credit-checked' is true.
- A filled order is an order for which 'order [credit-checked order] is filled' is true.
- ... and so forth.
Note on Notation The particular manner in which the unary fact types have been specified requires the states be strictly cumulative:
Organizing the states to be cumulative like this is not required, but seems useful for the example. |
The resulting state-oriented vocabulary for 'order' is a rich (and simple) one for verbalizing business rules — for example:
Business Rule: A credit-checked order must be verified by at least 3 references.
Business Rule: A shipped order must be assigned to a carrier.
Business Rule: An expeditor must be assigned to an order shipped but not invoiced for more than a week.
For an order to attain any given state, it must satisfy all business rules pertaining to that state. To say that differently, think of a state as reflecting a completed action. For the action to have been completed successfully, it must have satisfied all relevant business rules. Otherwise, it should fail. The following example illustrates.
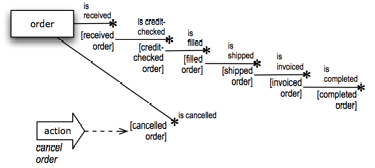
Figure 10. Fact model showing an 'unhappy' state of 'order'.
A new unary fact type worded 'order [cancelled order] is cancelled' appears in this diagram. This new fact type can be used to indicate that an order has been cancelled.
| Best Practice A best practice is modeling states is to avoid including 'unhappy' states such as this one within the 'happy life'. Such segregation yields the best results for expressing business rules. |
Presumably, canceling an order requires some action (or task or process). To illustrate, an action 'cancel order' has been added informally to the diagram. (Actions are not shown in proper fact models.)
The result the action seeks (a cancelled order) can come about only if business rules allow, for example:
Business Rule: A cancelled order must not have been shipped.
Under this business rule, the action can achieve the desired state cancelled order only if the order has not already been shipped. The state shipped order is therefore a prohibited antecedent.
Note that the business rule is not embedded in the action, but rather has been specified separately. Specification of business rules apart from processes is the essence of Rule Independence.
Coming full circle to points made earlier, every verb can be seen from two perspectives — as representing action (processes) or as representing knowledge. Invoking cancel order, a process, results in a cancelled order, a fact or bit of knowledge. Business rules fall naturally on the knowledge side. Once you liberate verbs from an exclusive process role, liberating the business rules is the next logical step. And what a powerful thing to do. So give us back our verbs!
References
[2] from Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary (emphasis added).![]()
[3] Pinker, Steven, The Stuff of Thought: Language as a Window into Human Nature, New York, NY, Viking, p. 31 (emphasis added).![]()
[4] Halpin, Terry (with Tony Morgan), Information Modeling and Relational Databases, (2nd Ed.), San Francisco, CA, Morgan Kaufmann, 2008. ![]()
[5] Nijssen, Sjir, An Architecture for Knowledge Base Software, Presentation at the Australian Computer Society Conference, July 1981. Available at: http://www.FBMf.eu ![]()
[6] Semantics of Business Vocabularies and Business Rules (SBVR) is a groundbreaking standard officially released in December, 2007 by the Object Management Group (OMG). For background on SBVR, refer to Ross, Ronald G. Ross, "The Emergence of SBVR and the True Meaning of 'Semantics': Why You Should Care (a Lot!) ~ Part 1," Business Rules Journal, Vol. 9, No. 3 (March 2008). URL: http://www.BRCommunity.com/a2008/b401.html![]()
[7] Business Rule Solutions, LLC (BRS) in Proteus, our methodology for business analysis, decisioning, and business rules. ![]()
[8] The Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary definition of objectify is [1a]: to cause to become or to assume the character of an object. ![]()
[9] from Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary (emphasis added). ![]()
# # #
About our Contributor:
Online Interactive Training Series
In response to a great many requests, Business Rule Solutions now offers at-a-distance learning options. No travel, no backlogs, no hassles. Same great instructors, but with schedules, content and pricing designed to meet the special needs of busy professionals.










How to Define Business Terms in Plain English: A Primer
How to Use DecisionSpeak™ and Question Charts (Q-Charts™)
Decision Tables - A Primer: How to Use TableSpeak™
Tabulation of Lists in RuleSpeak®: A Primer - Using "The Following" Clause
Business Agility Manifesto
Business Rules Manifesto
Business Motivation Model
Decision Vocabulary
[Download]
[Download]
Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules